Docker follows client-server architecture. Its architecture consists mainly three parts.
1) Client: Docker provides Command Line Interface (CLI) tools to client to interact with Docker daemon. Client can build, run and stop application. Client can also interact to Docker_Host remotely.
2) Docker_Host: It contains Containers, Images, and Docker daemon. It provides complete environment to execute and run your application.
3) Registry: It is global repository of images. You can access and use these images to run your application in Docker environment.
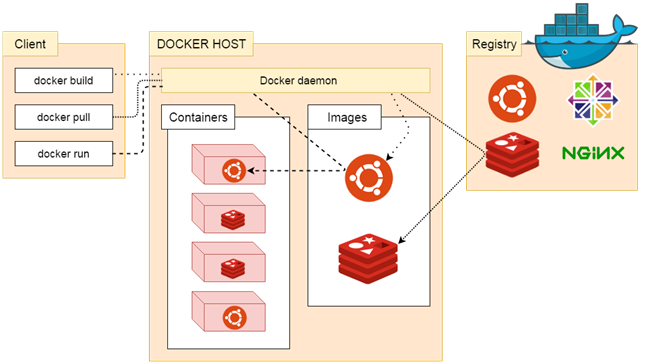
The Docker daemon
It is a process which is used to listen for Docker API requests. It also manages Docker objects like: images, container, network etc. A daemon can also communicate with other daemons to manage Docker services.
The Docker client
The Docker client is the primary way that many Docker users interact with Docker. When we use commands such as docker run, the client sends these commands to docker d, which carries them out. The docker command uses the Docker API.
Docker Registries
Docker registry is used to store Docker images. Docker provides the Docker Hub and the Docker Cloud which are public registries that anyone can use. Docker is configured to look for images on Docker Hub by default.
When we use the docker pull or docker run commands, the required images are pulled from your configured registry. When you use the docker push command, your image is pushed to your configured registry.
No comments:
Post a Comment